https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2104191118
chat-gpt summary
After re-analyzing the article "Topological braiding of cellular membranes" by Nikita N. Fakhri et al., I provide a more in-depth summary:
Main Findings
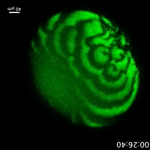
1. Topological Braiding: The researchers discovered that the plasma membrane of cells exhibits non-trivial topological features, which can be described as braids. These braids are formed by the intersection of membrane tubules and are stabilized by the cytoskeleton.
2. Cytoskeletal Stabilization: The braids are stabilized by the cytoskeleton, which provides mechanical support and maintains the topological features. The researchers found that the cytoskeleton plays a crucial role in regulating the formation and stability of the braids.
3. Dynamic Reorganization: The braids can undergo dynamic reorganization in response to changes in the cellular environment. This reorganization is mediated by the cytoskeleton and can lead to changes in the topological features of the membrane.
Theoretical Framework
1. Topological Invariants: The researchers used topological invariants, such as the linking number, to characterize the braids. These invariants provide a quantitative measure of the topological features of the membrane.
2. Membrane Mechanics: The researchers developed a theoretical framework to understand the mechanical properties of the membrane and its role in maintaining the topological features. This framework takes into account the elasticity and viscosity of the membrane.
Experimental Methods
1. Live-Cell Imaging: The researchers used live-cell imaging techniques, such as fluorescence microscopy, to visualize the plasma membrane and cytoskeleton of cells.
2. Image Analysis: The images were analyzed using computational tools, such as machine learning algorithms, to identify and characterize the topological braids.
3. Single-Particle Tracking: The researchers used single-particle tracking to study the dynamics of individual membrane proteins and their role in maintaining the topological features.
Biological Implications
1. Cell Signaling: The topological braids may play a role in cell signaling and communication, by providing a unique platform for protein-protein interactions.
2. Cell Migration: The braids may influence cell migration and adhesion, by regulating the formation of membrane protrusions and adhesion sites.
3. Cell Division: The topological features of the membrane may play a role in regulating cell division, by influencing the formation of the cleavage furrow.
Future Directions
1. Multiscale Modeling: The researchers suggest that multiscale modeling approaches, which integrate molecular, cellular, and tissue-level processes, are needed to fully understand the biological implications of topological braiding.
2. In Vivo Studies: The researchers propose that in vivo studies, which examine the behavior of cells in their native environment, are necessary to validate the findings and explore the biological implications of topological braiding.
3. Theutic Applications: The researchers suggest that understanding the role of topological braiding in cell biology may lead to the development of novel theutic strategies, such as targeting specific membrane proteins or pathways to modulate cell behavior.
>about text is AI generated summary of the paper
>I think that this paper is a very important scientific discovery, and biophysics binoculars helped us to see so deep into the existence that we can see waves on cell wall with naked eyes
>but it has ethical conundrum, starfish eggs was mutilated for unjustified use, stem cell research can harm society in very dangerous ways
>this paper talks about information processing in between cell or as we generally call it ***”consious experience”***
>if underlying phenomena of how these spiral waves on cell wall form can be theorised, it can help understand reverse aging and immortality